Algebraic Logic Unit
The algebraic logic unit performs operations analogous to an arithmetic unit in a CPU.
This component of the VM circuit evaluates both base-2 arithmetic operations and prime-field operation. It takes its input/output from the intermediate registers in the state controller.
The following block diagram maps out a draft of the internal components of the "ALU"
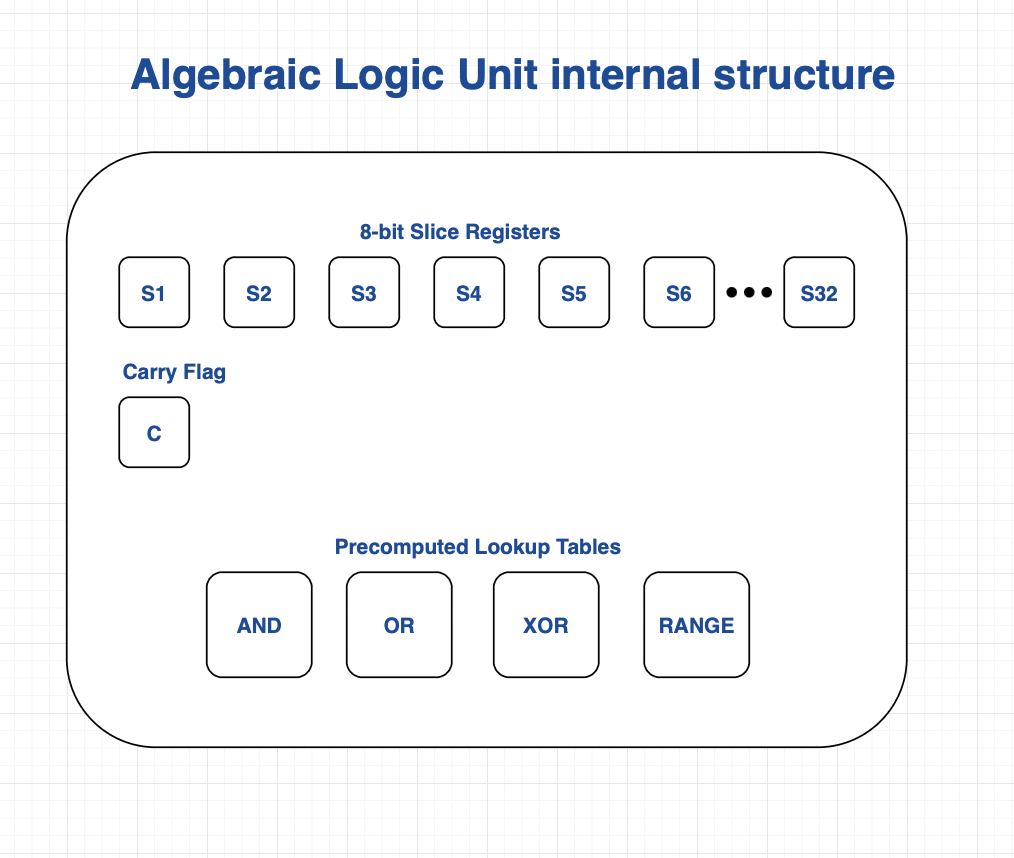
Notes:
For logic operations (e.g. AND/OR) we use lookup tables. The max. size of each lookup table cannot grow too large as the Prover pays a constant cost linear with the size of the lookup table.
To this end we use lookup tables for logic operations that take 8-bit input operands for a total table size of 2^16.
i.e. the table contains the output for every possible 8-bit combination of 2 input operands.
Slice registers
We need to slice our inputs into 8-bit chunks for logic operations, in order to index the lookup tables.
As a simplification, we can say that any operation that requires range-constraints will split the input operands into 8-bit slices, as we can then apply consistent range-checking logic.
Carry flag
Used to test for overflows. If we want the high-level instruction set to have "add with carry" we need to expose the carry flag to the state controller.
Example operation: 32-bit ADD(a, b, c)
Assume we start with a in intermediate register R1, b in intermediate register R2, and c in intermediate register R3
- Store the first 32 bits of
a + bin slice registerss1, s2, s3, s4, with the carry bit incarry - Validate
- Validate